Service As A Software – What Is SaaS And Why Do You Need It?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is rapidly becoming the dominant consumption and delivery model for enterprise apps. With SaaS, users access applications over the Internet using a standard web browser such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox rather than a locally stored installation.
By eliminating the need to install and run applications on your own computer, SaaS is transforming the way we consume applications. Unlike traditional software, SaaS applications are centrally hosted and managed, typically by the software provider.
Settings and preferences are stored remotely and synchronized automatically, so users can access their files from any computer using their log-in credentials.
Remember the days when you had to buy a heavy program and install it on your desktop PC or business network to run and update? If you have experienced bad software, full of bugs and errors, installation problems, crashes and slow performance, then you probably know that software can be quite frustrating, but software as a service can eliminate that frustration.
What Is Software As A Service (SaaS)?
Software as a Service, also known as Software on Demand, is a software distribution and licensing model in which access to the software is provided on a subscription basis, with the software being centrally hosted.
It is an alternative to traditional software licensing and distribution models that require companies to purchase licenses to install and run their software locally on each computer in the network.
SaaS is one of three important categories of cloud computation, alongside platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
As organizations become increasingly reliant on cloud-based computing, the use of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) to meet their needs has increased. Software as a service lets all your employees have access to the application via a browser instead of each employee downloading and installing the software on their PC individually.
SaaS offers a variety of advantages over traditional software – including greater access to apps for employees, reduced capital and personnel investment, and lower maintenance costs.
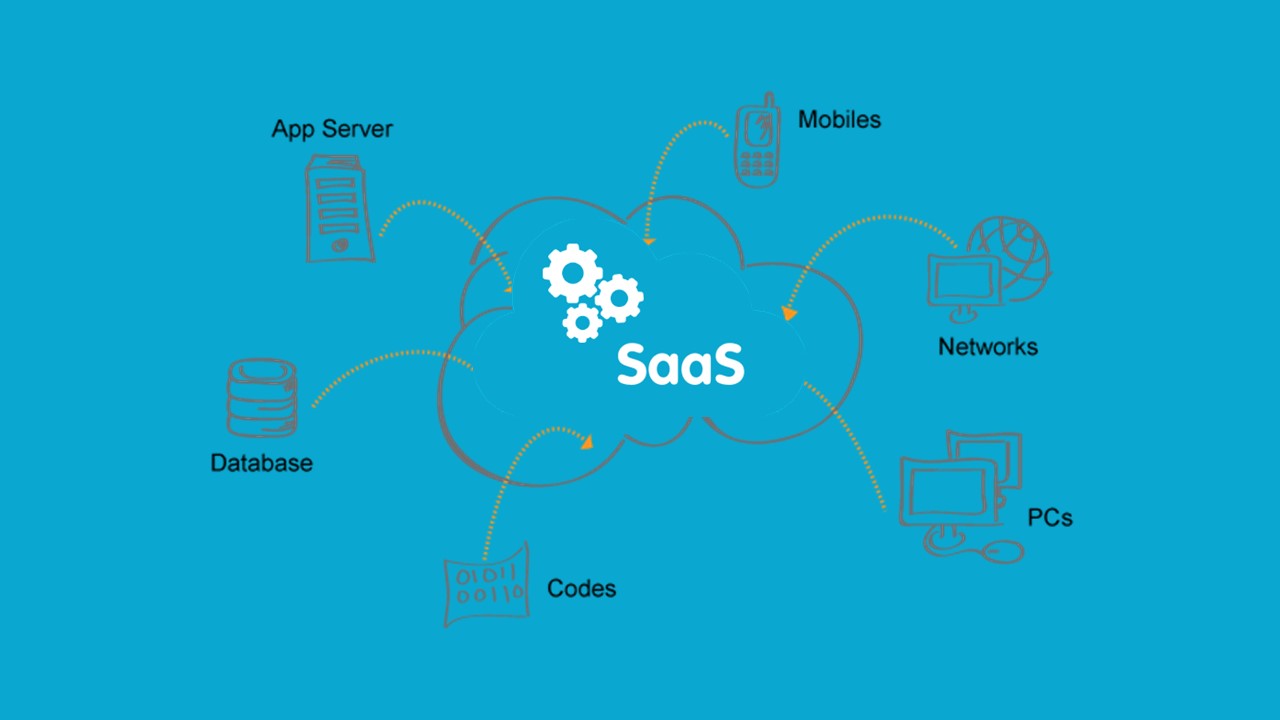
How Does Software As A Service Work?
Today, SaaS is the preferred method for users to access applications and data. There is no longer a need for the user to install software on their devices. Instead, users can log in through any computer with Internet access to get up-to-date versions of the software and their files.
SaaS offers a centralized computing solution that stores all software, data and services on the cloud. This enables users to access them from any internet-connected device, provided they have the proper login credentials.
Additionally, SaaS means everyone is using the same version of the software, which can make it easier to share documents and collaborate with coworkers. Ongoing maintenance and security updates to the software are also done automatically.
Using SaaS can be less expensive than purchasing off-the-shelf software because companies only pay for licenses they use, with no upfront costs.
SaaS offers a way for companies to save time and money by subscribing to software that is accessed through the Internet. Users of a SaaS service typically sign up for an account and then log in to access the service, making it easy to use the software on multiple different devices that are connected to the Internet.
History Of SaaS
Origins of SaaS can trace its roots to a theory called time-sharing, which was popular in the late 1950s and early 1960s. While it was rumored to have been one of the largest innovations at the time and found to be cost-effective for smaller businesses, time-sharing was made less useful by the growth of personal computers (PCs).
As PCs grew in popularity, companies slowly transitioned from time-sharing over to a system in which each machine was owned and controlled individually.
Over the past 20 years, software-as-a-service (SaaS) has gone from an experiment to a ubiquitous part of the enterprise. Today, SaaS is driving digital transformation for every industry by making it easier for organizations to develop and customize products and services without tearing anything down and starting from scratch.
Common SaaS Scenarios
If you’ve ever logged into an email account from a web browser, you’ve used software as a service (SaaS). Another example is Google Apps for Business, which includes Gmail, Google Docs, and Google Hangouts. You can rent these applications by the month or by the number of users.
For businesses, SaaS applications that enable productivity and collaboration are available in a variety of forms. Take SalesForce.com, for example. It’s a service that provides businesses with an easy-to-use CRM system. When you sign up for the service, you pay a subscription fee to use it, and the software runs on Salesforce.com’s own servers rather than on your own computer.
The SaaS provider manages the licenses, software installation and upgrades, ensuring that you always have the latest version. With SaaS, your organization can access business-critical apps they need while reducing the overall costs of supporting an IT infrastructure on-premises.
Advantages Of SaaS In Cloud Computing
Software as a service offers a lot of advantages. Tome of the advantages of SaaS in cloud computing includes:
1. Access To Sophisticated Applications
SaaS is a ready-to-go web application for users. You don’t need to purchase, install, upgrade, or maintain any hardware, software or middleware. SaaS makes enterprise applications like CRM and ERP affordable for companies of all sizes and makes it possible to distribute applications to large numbers of users at the place they are needed — on the Web.
2. Pay For What You Use Only
SaaS applications are always evolving, and this means you always get the most current version of the software. You conserve money because the SaaS service scales up and down automatically according to your usage levels. And, you only pay for what you use.
3. Use Free Client Software
Benefit from the latest security updates, without worrying about installing software on all your business users’ devices. Since you don’t need to install anything with SaaS apps, you can access them directly from their browser. Most of the time you don’t even need plugins on your system.
4. Mobilize Your Workforce Easily
Software as a Service (SaaS) is changing the way companies mobilize their workforces. With the ability to access SaaS applications and data from any internet-connected computer or mobile device, users can now be productive when on the go.
Organizations don’t need to worry about developing apps to run on different types of computers and devices because the service provider has already done so. In addition, it’s easier for companies to manage security issues inherent in mobile computing when a carefully chosen service provider is handling data security.
5. Access App Data From Anywhere
Now cloud-enabled, your app data can be accessed on any device and computer, whenever, wherever. Even if your computer or mobile device fails, the cloud retains all of your data.
6. Market Reach
One of the main advantages of cloud computing is that it allows access to information on-demand from anywhere and from any device, so employees can be more effective. Also, users no longer have to worry about investing in hardware, software and services. With cloud computing companies only pay for what they use.
7. Data And Analytics
With SaaS software, data is stored in the cloud rather than on devices. That means everything is run through a centralized platform, which makes it possible to leverage the power of data and analytics.
Businesses using SaaS software can easily gather data and provide it for analytics use, which gives them valuable insights into their business operations. This lets them streamline their workflows and make efficiency savings that positively impact their bottom line.
8. Customization
SaaS applications offer a high degree of flexibility, making it easier for you to customize the solution to meet your specific business needs and requirements.

Disadvantages of Service As A Software
Just as we have a lot of software as a service advantage, we also have SaaS disadvantages too. Here are the few disadvantages of SaaS:
1. Problems Beyond Customer Control
There may be many factors beyond a customer’s control when using SaaS. Issues can arise from service disruption, unwanted service changes or security breaches that cause customers to lose access to their SaaS accounts, work and resources.
Customers should make sure their providers’ SLA is being enforced. They may also need to look into other agreement options.
2. Customers Lose Control Over Versioning
Applications in SaaS may be upgraded by the provider without your organization’s consent. This is generally easier for the organization, but a new version of an application may require that your organization provide extra time and resources for training if it adopts a new version of an application.
3. Difficult To Switch Vendors
When you choose a cloud computing provider, you face the risk of becoming locked in to that provider. Cloud lock-in occurs when a customer cannot easily transition between service providers due to proprietary technologies, data types, and/or imperfect portability of data.
If your business is already heavily invested in a particular vendor, it may be more difficult to later switch to another vendor.
4. Security
Security concerns continue to be major barriers to the growth of cloud computing and IT outsourcing.
Your SaaS applications are hosted in the cloud, often by a third party. Your data may come from internal sources or external ones provided through APIs. In either case, you want to be sure that it is protected and secured.
Software As A Service Examples
There are many software as a service examples vendors providing a wide range of products and services. Some key examples of SaaS vendors include Google, Amazon, and Oracle.
SaaS products range from IT business analytics tools to video streaming services. There are SaaS applications for business applications like email, sales management, financial management, customer relationship management (CRM), human resource management (HRM), collaboration and billing.
There are also Enterprise Software as a Service products for specific industries like insurance or medical, which are known as vertical SaaS products.
Here is more software as a service example:
- Salesforce
- Microsoft 365
- Trello
- Netflix
- Google Workplace apps
- HubSpot
- Zendesk
- Slack
- Zoom
- DocuSign
- Adobe Creative Cloud
- Mailchimp
- Spotify
- Zoho WorkDrive
- Basecamp
- Halo Recognition
- Dropbox
- Cisco WebEx
- GoToMeeting
- SAP Concur
- Lumen5
- Canva
- ZenDesk
- Visme
- Box
- Amazon Web Services
- Buffer
- Squibler
- FutureFuel
- Donorbox
Software as a Service Pricing / SaaS Pricing
In traditional software licensing, the customer would pay for a license and then the software company would deliver and install the software on the customer’s hardware.
This is generally not the case with SaaS products. SaaS providers usually use one of the different subscription-based pricing models for customers.
They are less expensive than traditional software licenses for enterprise software, as setup and installation onto hardware are not necessary. The subscription-based model is also often more flexible for customers.
The customer only has to pay for the services that they are using at any given time, and they can decide to pay for a monthly, annual or one-time subscription.
- Flat Rate: Customers get access to the software’s full suite for a fixed monthly or annual subscription fee.
- Ad-based or Free: A software may be completely free for users but the providers usually generate revenue from such software through advertisement. There is usually an upgrade option to eliminate ads.
- Per-User: Pricing may be determined by the number of people that will be using the service. There is always a fixed price for every user.
- Storage tiers: Users may have free access to the service but will be required to pay for more storage after exceeding the free limit.
- Per user tier: Pricing will be based on the number of users on the subscription.
- Pay as you go: Here, the price is based on the number of features the subscriber needs.
- Per active user: This pricing model combines pay as you go and per-user pricing. Users are billed per user, but only if the user is using the service actively beyond a defined threshold.
- Feature-based: The price is determined based on the features accumulated by the subscriber.
- Freemium: The service will be free but there is room for upselling.

SaaS Vs. IaaS Vs. PaaS
SaaS is one of the three most important cloud service types, along with IaaS and PaaS. All three models involve cloud providers that provide hosted data center resources to consumers over the internet. The SaaS model is the most popular of the three, which is mostly due to its flexibility and potential for scalability.
This model has been around since the late 1990s, and it is characterized as software as a service that is delivered over the internet.
SaaS is a software as a service, which is delivered all the time as a monthly subscription, whereas IaaS is a utility computing service, which is more like renting computing resources for a fixed amount of time.
IaaS is often associated with cloud computing, which is still a type of IaaS. PaaS is a development platform as a service, which is used to accelerate application development.
SaaS or Software as a Service is a type of software application that can be accessed over the internet. The software is hosted on a remote computer, accessed by the user, and managed by the vendor. In other words, the vendor handles everything related to the software.
There is no need to download anything, manage any existing IT infrastructures, or even deal with any aspect of the software management. The vendor handles everything.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) is a service that provides computer resources, such as servers, storage, and networking hardware, to companies. The process of implementing an IaaS service requires the customer or organization to manage its own computer resources and to make sure the required infrastructure components are in place.
When it comes to app development, PaaS provides a framework of resources to enable organizations to build customized apps with a high level of performance and flexibility. The vendor manages the resources that the apps need to function.
The PaaS is applied to any service that provides a framework of resources for an organization’s in-house developers. It consists of a hosted platform that enables developers to create customized applications. The vendor oversees the data center resources that support the tools.
Paas Meaning (Platform As A Service)
PAAS is an acronym for Platform as a Service. It is a cloud computing service that provides the infrastructure and platform for software applications.
It can be offered on a monthly or yearly basis, depending on the vendor. The PAAS provider then manages the hardware, operating system, database, middleware and other services that are required to run the application.
Saas In Cloud Computing
Software as a service (SaaS) is a software distribution model in which the customer accesses the software in a cloud computing environment.
The term SaaS is used to describe any software that is delivered over the Internet and accessed from a remote location.
This includes web-based office applications, email, online storage and file-sharing services, customer relationship management (CRM) applications, and many more.
The benefits of SaaS are that it provides access to an application or service without having to install it on your own computer. It’s also more cost-effective for companies because they don’t have to buy servers or other equipment.
There are many different types of SaaS models as well, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Infrastructure As A Service
Infrastructure as a Service is a type of cloud computing that provides the necessary resources to run applications and store data.
It is typically used by small and medium-sized businesses, but can also be used by large enterprises.
The IaaS model can be used to run almost any application, as opposed to only running specific software packages on the same server.
IaaS is often referred to as “the cloud” because of the way it abstracts computing resources.
Some benefits of Infrastructure as a Service include scalability, reliability, and flexibility.
Saas Vs PaaS
SaaS (software as a service) is a model for delivering software over the internet.
It typically allows the user to access and use the software from a remote location so that the user does not need to install anything on their computer.
SaaS is sometimes referred to as “on-demand” or “cloud computing”.
Paas (Platform as a service) is also known as cloud computing and it provides users with an operating system and necessary applications that are hosted on a cloud network.
Paas offers its users scalability, flexibility, security, and reliability.
Cloud As A Services
Cloud computing is an IT model for enabling ubiquitous access to shared pools of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Cloud computing is a service that allows you to store your files online. There are many benefits of using the cloud such as being able to access your documents from anywhere you have an internet connection.
Also, it’s a cost-effective way to store your data because you only need to pay as you use it instead of having to buy hardware like hard drives and computers.

Software As A Service FAQs
What Is SaaS Marketing?
SaaS marketing refers to a method of marketing that focuses on the process of selling software as a service to potential consumers. SaaS marketing is different from other forms of marketing because it is not based on the traditional products that consumers buy, like physical or digital media.
SaaS marketing is centered on the software as a service that consumers pay for and is commonly associated with a subscription model. One of the primary goals of SaaS marketing is to get consumers to try out the software before they buy. SaaS marketing is often used to sell cloud-based software applications, but it can also be used to sell information services.
What Is B2B SaaS?
B2B SaaS encompasses a wide variety of software services that companies make available to their customers. These types of software products help organizations to optimize a wide variety of functions such as marketing, sales, and customer service.
How Is MRR Calculated for a SaaS Business?
For SaaS businesses, MRR is an important metric. MRR is calculated by multiplying the average revenue per customer by the total number of accounts for that given month. For example, if a SaaS business has 2,000 customers and each customer spends $50 per month on their service, the business would have an MRR of $100,000.
SaaS versus on-premise: How do I choose?
Choosing between an on-premise solution and a SaaS solution is a question that many businesses are faced with. Most businesses are faced with this decision because they either have existing software and do not have the expertise to create a new one or they have outgrown their current solution.
However, before you make this decision, you need to determine the complexity of your business. To do this, you will need to answer a few questions about your business.
- How special your business is compared to other businesses in your industry?
- What level of software customization are you after?
- What is your budget
- Who is the SaaS vendor?
- and so on
Can I Customize SaaS Software?
Business software, or Software as a Service (SaaS), is a solution that typically provides a wide variety of features. When you purchase a SaaS solution, such as Microsoft Office 365, you are able to use the software on any device, such as a computer, tablet, or smartphone.
SaaS software is often marketed as being a solution that is “set it and forget it”, meaning that it is easy to use and requires minimal maintenance.
You can customize your SaaS solution to match your specific needs and preferences, whether it is in the form of a UI or in the form of specific data fields. When you purchase a SaaS solution, you are often given the option of changing the software to suit your needs.
Who Owns My SaaS Data?
Most companies are still building their own SaaS apps and starting to use cloud-based services. However, there is still a lot of confusion around what happens to your information when you sign up for a service.
In general, the services that companies are building are still owned by the company and the company has rights to the data that is stored on the SaaS vendor servers. The service level agreement (SLA) is a contract between your company and the SaaS service provider that is particular to that provider.
The SLA describes the service that the company is providing and the service it is receiving, as well as the responsibilities of the provider and the customer.
The SLA also defines the service provider’s rights to the customer’s data. The SLA will often state that the customer owns the data stored on their company’s servers and they have the right to retrieve their data at any point.
Is My Data Safe In The Cloud?
There are many questions when it comes to cloud security, but one of the most important ones is “Is my data safe?” From the outside, it may seem that cloud storage is more secure than keeping data on your own computer.
However, many people are wary of this. There is a lot of talk about how secure data is in the cloud, but many people are still unsure. The truth is that when it comes to cloud providers, one of the most important things is to ensure that your data is safe.
They work hard to make sure that your data is safe, and they work even harder to ensure that your data will always be safe. The best way to do this is to make sure that your data is encrypted, and that it is stored in a highly secure location.
Many providers like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure offer highly secure locations that are monitored 24/7 by IT teams. If you would like to know more about the security of your data, you can contact the provider.
According to Gartner’s prediction, 99% of cloud security failures will be the user’s fault.
What If My Service As A Software Vendor Goes Out Of Business?
When a software vendor goes out of business, it’s always a good idea to keep your data. Even if the vendor was bought by a larger company, your data is still yours, and you have a right to it. This vendor failure is a good time to get backup copies of your data if you have a backup plan in place.
If you don’t have a backup plan, you may be able to transfer your data to another software vendor. This can be done by uploading the data to a central location that the software vendor offers, or by using a cloud service that the vendor offers.
However, you need to consider the following before you choose a SaaS vendor:
- How long has the Software as a service company been in business?
- Is the company growing in terms of customers and employees?
- Does the company have a technology roadmap?
The most significant thing is to be sure your SLA has a clause that declares that you can export your data, anytime, which is the norm today.
SaaS Product
SaaS products are software-as-a-service that can be accessed by a user with a browser. These products can be used as standalone applications or integrated into other applications.
The benefits of SaaS products are that they have low upfront costs, low maintenance costs, and high scalability. The downside is that the user needs to pay for the product on a monthly basis and it is not easy to switch providers if the service is not meeting their needs.
SaaS versus cloud: What’s the big difference?
Software as a service (SaaS) is a type of software that is delivered over the internet. It is different from cloud software in that SaaS is typically purchased on a subscription basis. The buyer stays on their own computer and only accesses their software through the internet.
The cloud refers to anything that’s hosted remotely and delivered via the internet. While all cloud programs are run by underlying software, SaaS refers specifically to business software applications that are delivered via the cloud. SaaS is a specific type of cloud computing.
Today, almost every core businesses function is available via SaaS providers.
Conclusion
service as software is a service provided by software and computer developers that allows enterprises to securely access, manage, and automate their software applications and their data. In return, the service provider is able to offer the tools that the enterprise needs to become more efficient and provide better services to the market.
Overall, SaaS offers many benefits that should work in the interests of the suppliers and users. While several enterprises might choose to set up their own cloud management services and use arrangements between devices and sites to control their data, the bulk of small businesses would be better off using SaaS.